In this article, you will learn what Linked Lists are and how they work. Linked Lists come in various forms, including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists.
Linked List is referred to as a collection of data elements called nodes which can be added or removed dynamically. Linked List is a data structure which can also be used to implement other data structures such as stacks, queues and so on.
Linked List Real World Example

As you can see above image represents the example of Linked List where rail engine (locomotive) denotes the head / start / root node whereas the last bogie denotes the end (last node) of linked list.
Types of Linked Lists
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Singly Linked List
Singly Linked List is the simplest type of linked list in which every node has two components:
- Data: As the name suggests, it holds or stores the data.
- Link: A reference or link to next node. It is a pointer to another node of same type, it is also known as
self-referentialdata type.
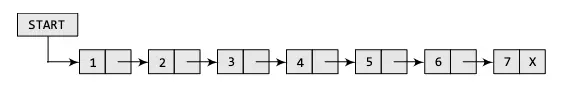
Now, the reason it is called singly because it has single reference or link which allows you to traverse in one direction only. In simple words, you can say that singly linked lists are unidirectional.
Every node holds data and address of next node except the last node which holds NULL to indicate the end of linked list.
Doubly Linked List
Doubly Linked List is a bit complex type of linked list which stores address to both previous and next nodes. Therefore, it has 3 components: data, pointer to previous node, pointer to next node.
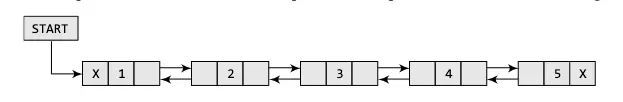
The reason it is called doubly because it has two references or links which allows you to traverse bidirectional (forward and backward).
Circular Linked List
Circular Linked List is quiet similar to singly or doubly linked list but the only difference is, the (next) link part of the last node points to or contains the address of head / root / start node.
Note: We can use both singly linked list or doubly linked list to create circular linked list.
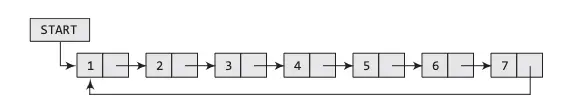
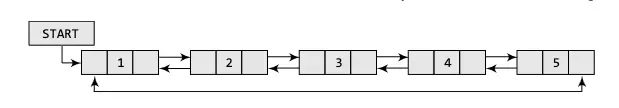
Linked List Operations
- Insert Operation
- Insert node at first
- Insert node at last
- Insert node at specified location
- Delete Operation
- Delete first node
- Delete last node
- Delete specified node
- Traversal
- Sorting
- Splitting
- Merging
- Counting (Total Nodes, Odd-even number of nodes)



Comments